Harnessing the Potential of Photobiomodulation for Obesity Management
Optimizing Metabolic Health: Harnessing the Potential of Photobiomodulation for Obesity Management
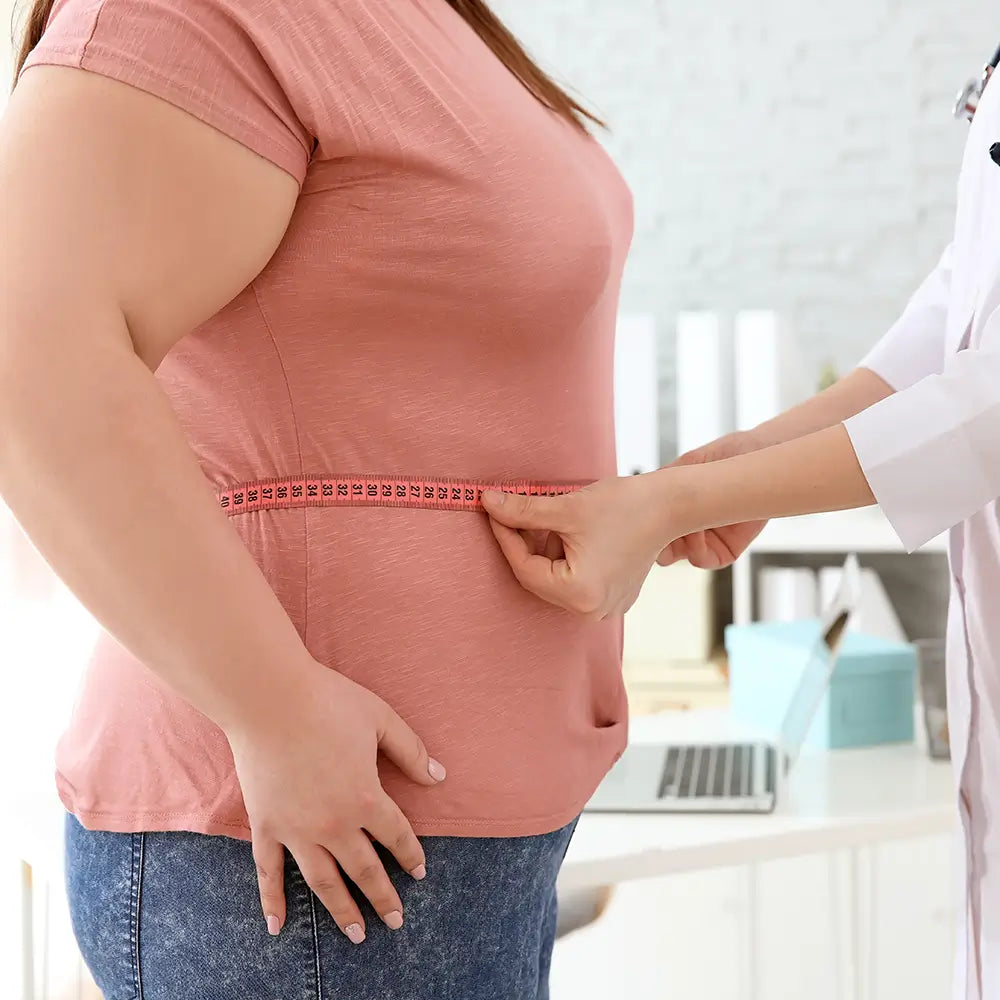
The global rise in obesity rates poses a significant problem for public health, leading to increased research endeavors aimed at discovering innovative treatments that address the root causes of metabolic dysfunction. Against this backdrop, photobiomodulation (PBM), also known as red light therapy, has emerged as a promising approach that could potentially transform the management of obesity. This comprehensive analysis explores the complex relationship between adipocyte physiology, metabolic dysregulation, and the potential therapeutic benefits of PBM in the fight against obesity and its related health complications.
Adipocyte Dysfunction: A Intersection of Metabolic Derangement
At the heart of metabolic dysregulation caused by obesity lies the complex interaction between malfunctioning adipocytes, the main cellular components of adipose tissue, and systemic metabolic disturbances. In normal physiological conditions, adipocytes play a crucial role in maintaining energy balance by regulating lipid storage, hormone release, and inflammatory signaling. However, in the presence of obesity, the enlargement and increased number of adipocytes disrupt this delicate balance, leading to the abnormal release of adipokines, pro-inflammatory cytokines, and reactive oxygen species (ROS). These irregular behaviors of adipocytes trigger a series of harmful events, such as insulin resistance, chronic inflammation, dyslipidemia, and endothelial dysfunction, all of which contribute to the development of metabolic issues associated with obesity.
Understanding the Science of Photobiomodulation
Photobiomodulation is a technique that utilizes low-level laser or LED therapy to activate cellular processes, encouraging tissue repair and regeneration. Red and near-infrared light wavelengths penetrate the skin at a cellular level, where they are absorbed by mitochondrial chromophores like cytochrome c oxidase. This absorption triggers a series of photochemical reactions that ultimately boost mitochondrial respiration, ATP production, and antioxidant defenses. Additionally, it helps regulate inflammatory pathways and gene expression. By improving cellular metabolism and reducing oxidative stress, PBM shows great potential as a non-invasive approach to enhance metabolic health and address metabolic issues associated with obesity.
Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of PBM in Obesity Management
Recent studies, both in preclinical and clinical settings, have presented compelling evidence that supports the therapeutic effectiveness of PBM in mitigating metabolic abnormalities associated with obesity. By utilizing specific wavelengths of light to target adipose tissue, PBM has demonstrated its ability to facilitate the remodeling of adipocytes, enhance lipid metabolism, and alleviate insulin resistance. Additionally, PBM has been found to modulate inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress markers, leading to a reduction in chronic low-grade inflammation and an improvement in endothelial function. These diverse effects highlight the potential of PBM as a versatile and comprehensive approach to managing obesity, providing a non-pharmacological alternative or complement to traditional interventions.
Navigating the Clinical Landscape: Integration of PBM into Obesity Management Protocols
Incorporating PBM into Obesity Management Strategies: Enhancing metabolic health through the integration of PBM into comprehensive treatment plans for obesity presents a promising avenue for addressing the intricate metabolic factors contributing to this condition. By targeting adipocyte metabolism, insulin sensitivity, systemic inflammation, and oxidative stress, PBM offers a versatile therapeutic approach that can be customized to meet the unique needs of each patient. Its non-invasive nature also makes it a suitable complement to dietary modifications, physical activity regimens, and medication, leading to improved treatment results and sustained metabolic well-being in the long term.
Challenges and Opportunities in Translating PBM Research into Clinical Practice
Despite the promising preclinical and clinical evidence supporting the therapeutic potential of PBM in obesity management, several challenges and opportunities lie ahead in translating research findings into clinical practice. Optimizing treatment parameters, standardizing protocols, and elucidating the long-term effects of PBM on metabolic health are critical areas that warrant further investigation. Additionally, addressing regulatory and reimbursement challenges, as well as enhancing public awareness and acceptance of PBM as a therapeutic modality, are essential steps in facilitating its widespread adoption in clinical settings. Collaborative efforts among researchers, clinicians, policymakers, and industry stakeholders are paramount in overcoming these challenges and harnessing the full potential of PBM in combating the global obesity epidemic.
Conclusion: Unlock the Potential of Photobiomodulation for Optimal Metabolic Health
In conclusion, the revolutionary potential of photobiomodulation in enhancing metabolic health and addressing metabolic issues linked to obesity signifies a groundbreaking advancement in modern healthcare. Through utilizing specific light wavelengths to regulate cellular functions, reduce inflammation, and support tissue healing, PBM introduces an innovative and impactful strategy for managing obesity. As we navigate the intricate web of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors influencing obesity, the enlightening effects of red and NIR light therapy provide a beacon of hope for individuals worldwide struggling with obesity and its metabolic consequences. By embracing the possibilities of PBM, we can pave the path towards a future characterized by metabolic strength, energy, and overall wellness.

PRUNGO MODULE
The Prungo Module effectively alleviates joint pain, reduces inflammation, and promotes the healing of damaged tissues.
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.
!